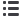
Securities Lending Transactions Accounted for as Secured Borrowings
2015
Remaining Contractual Maturity of the Agreements
(In millions)
Overnight
and
Continuous
(1)
Up to 30
days
Total
Securities lending transactions:
Japan government and agencies
$
0 $
499 $
499
Public utilities
108
0
108
Banks/financial institutions
13
0
13
Other corporate
321
0
321
Total borrowings
$
442 $
499 $
941
Gross amount of recognized liabilities for securities lending transactions
$
941
Amounts related to agreements not included in offsetting disclosure in Note 4
$
0
(1)
These securities are pledged as collateral under our U.S. securities lending program and can be called at our discretion; therefore,
they are classified as Overnight and Continuous.
We did not have any repurchase agreements or repurchase-to-maturity transactions outstanding as of December 31,
2016 and 2015, respectively.
Certain fixed-maturity securities can be pledged as collateral as part of derivative transactions, or pledged to support
state deposit requirements on certain investment programs. For additional information regarding pledged securities
related to derivative transactions, see Note 4.
At December 31, 2016, debt securities with a fair value of $17 million were on deposit with regulatory authorities in the
United States (including U.S. territories) and Japan. We retain ownership of all securities on deposit and receive the
related investment income.
For general information regarding our investment accounting policies, see Note 1.
113
4. DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
Our freestanding derivative financial instruments have historically consisted of: (1) foreign currency swaps and credit
default swaps that are associated with investments in special-purpose entities, including VIEs where we are the primary
beneficiary; (2) foreign currency forwards and options used in hedging foreign exchange risk on U.S. dollar-denominated
investments in Aflac Japan's portfolio; (3) foreign currency forwards and options used to hedge foreign exchange risk from
our net investment in Aflac Japan and economically hedge certain portions of forecasted cash flows denominated in yen;
(4) swaps associated with our notes payable, consisting of cross-currency interest rate swaps, also referred to as foreign
currency swaps, associated with certain senior notes and our subordinated debentures; and (5) options on interest rate
swaps (or interest rate swaptions) and futures used to hedge interest rate risk for certain available-for-sale securities. We
do not use derivative financial instruments for trading purposes, nor do we engage in leveraged derivative transactions.
Some of our derivatives are designated as cash flow hedges, fair value hedges or net investment hedges; however, other
derivatives do not qualify for hedge accounting or we elect not to designate them as an accounting hedge. We utilize a net
investment hedge to mitigate foreign exchange exposure resulting from our net investment in Aflac Japan. In addition to
designating derivatives as hedging instruments, we have designated the majority of the Parent Company's yen-
denominated liabilities (notes payable and loans) as non-derivative hedging instruments for this net investment hedge.
Derivative Types
We enter into foreign currency swaps pursuant to which we exchange an initial principal amount in one currency for
an initial principal amount of another currency, with an agreement to re-exchange the currencies at a future date at an
agreed upon exchange rate. There may also be periodic exchanges of payments at specified intervals based on the
agreed upon rates and notional amounts. Foreign currency swaps are used primarily in the consolidated VIEs in our Aflac
Japan portfolio to convert foreign-denominated cash flows to yen, the functional currency of Aflac Japan, in order to